Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) Technology
The spark plasma sintering (SPS) method [1,2,3,4,5] is the state-of-the-art sintering technique widely used for densification of various ceramic, metallic and polymer materials mainly because of the very short sintering time compared to other known techniques. In the SPS method, the current flows through conductive (usually graphite) dies and the powder inside them (if conductive), which is additionally compressed. The powder is heated by the released Joule heat at the point of contact between the particles of the conductive powders and/or the Joule heat generated in the dies. In assumption, the mass transfer by evaporation and condensation as a result of the plasma discharge in the pores between the grains of powder is also increased.
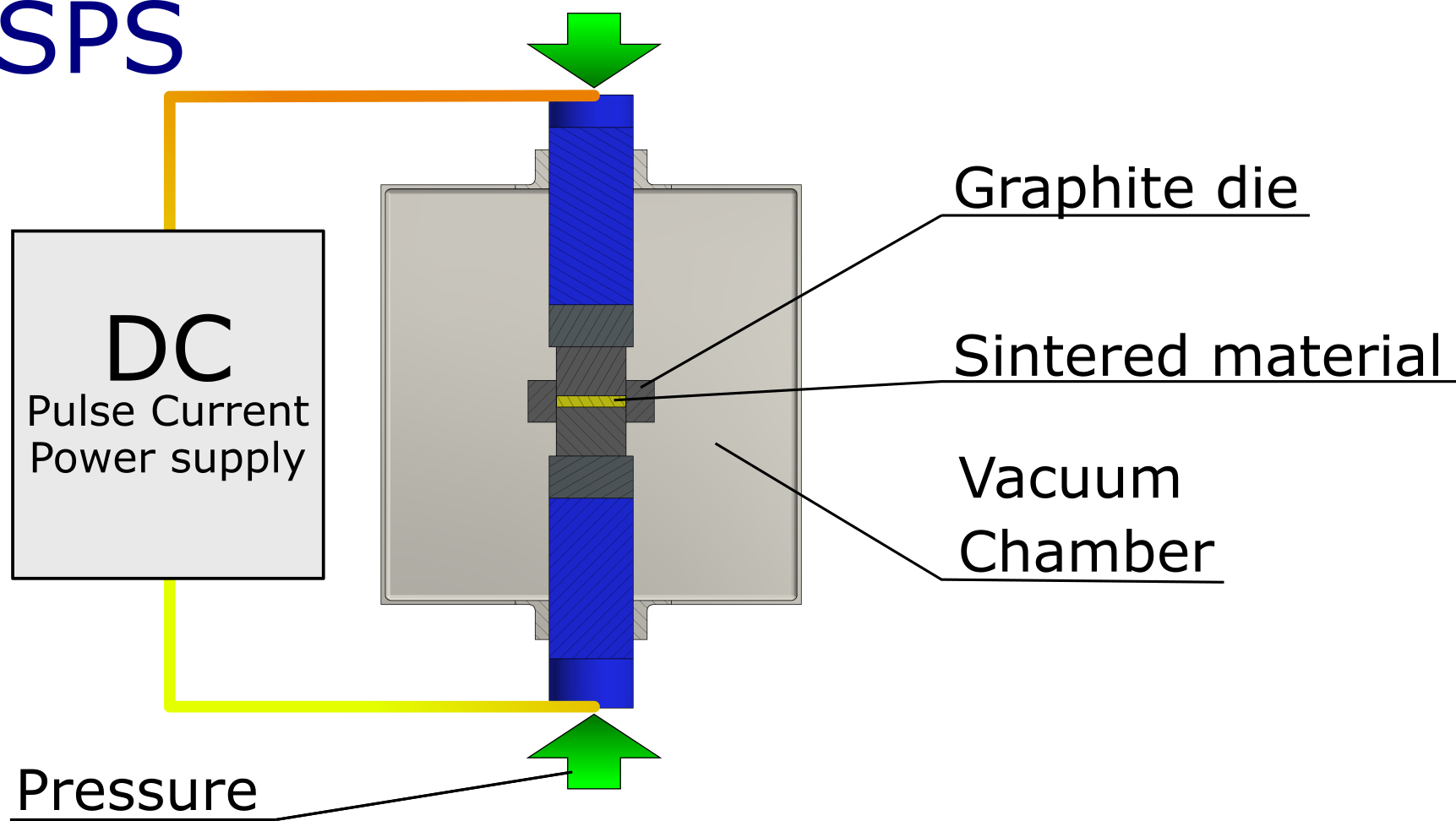
Fig. A scheme of SPS device.
The SPS method enables the use of very high heating rates (up to 1000 K∙min-1 [6]), significantly shorter time of the entire process, lower pressure, and in many cases also lower temperature of the sintering process [7,8,9] compared to the conventional sintering methods. In addition, by placing the thermocouple directly in the die, it allows perfect control over the conditions of the sintering process. Moreover, due to the shortening of the entire process time, there is no significant grain growth, which is particularly important in the case of densification of nanocrystalline materials [10].
